29
2025
-
05
2024 Annual Quality and Integrity Report
2024 Quality and Integrity Report
Company Name: Zhejiang Shangyou Cutting Tools Co., Ltd.
Compilation Date: February 2025
Compiler: Wang Qiang
1
Contents Table of Contents
Preface....................................................1
I. Company Profile.............................................3
II. Quality Philosophy.............................................3
III. Enterprise Quality Management.........................................6
(I) Quality Management Organization.......................................6
(II) Quality Management System......................................12
(III) Quality and Safety Risk Management..................................14
(IV) Quality and Integrity Operation Management..................................16
(V) Marketing Management..........................................20
IV. Quality Management Foundation........................................21
(I) Standard Management..........................................21
(II) Metrology Management..........................................21
(III) Certification Management..........................................22
(IV) Inspection and Testing Management......................................22
V. Product Quality Responsibility........................................23
(I) Product Quality Level......................................23
(II) Product After-Sales Responsibility......................................24
(III) Corporate Social Responsibility......................................25
(IV) Quality Credit Record......................................31
VI. Report Conclusion............................................32
2
Preface Foreword
This report is the first publicly released "Enterprise Quality and Integrity Report" of Zhejiang Shangyou Cutting Tools Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Shangyou," "our company," or "the company"). It is compiled in accordance with the provisions of the national standards of the People's Republic of China GB/T 29467-2012 "Implementation Specification for Enterprise Quality and Integrity Management" and GB/T 31870-2015 "Guideline for Writing Enterprise Quality Credit Report," and the company's 2024 quality and integrity system construction situation.
Our company guarantees that the information contained in this report does not contain any false records or misleading statements, and assumes responsibility for the authenticity and accuracy of its content.
Report Scope:
The organizational scope of this report is Zhejiang Shangyou Cutting Tools Co., Ltd. This report describes the company's concepts, systems, measures, and performance in quality management, product quality responsibility, and quality and integrity management from January 2024 to December 2024.
Report Publication Format:
Our company publishes a quality credit report annually. This report is published to the public in the form of a PDF electronic document on the company's website (http://www.shangyoutools.com). We welcome you to download, read, and provide valuable feedback.
3
General Office Statement
To ensure responsibility to customers and the scientific, fair, and effective inspection and testing, and to provide an independent and objective evaluation of testing quality with true and reliable testing data, the company's responsible person makes the following statement:
(1) Strictly abide by national laws, regulations, and policies on quality, adhere to a scientific and fair stance, strictly implement standards, and bear legal responsibility for the data provided.
(2) The company has established a quality system in accordance with GB/T 19001-2016/ISO 9001:2015 quality management system. In various quality activities, it strictly follows the procedures and methods stipulated in the "Quality Manual," implements full-process and full-element control over the quality of testing work, and can ensure the accuracy and reliability of the testing results.
(3) Independently conduct testing work, possess high-quality testing personnel and other hardware resources, and can provide "scientific, fair, accurate, and efficient" testing technology. In the testing work, it is not subject to any interference from administrative, commercial activities, or financial matters. It is not controlled by economic interests and ensures the independence and integrity of testing at all times.
(4) Strictly abide by the principle of confidentiality and relevant regulations, and be responsible for the authenticity of the test data.
(5) Strictly be responsible to customers, strictly implement various internal standards, and ensure product quality.
Chief Quality Officer Certificate and Oath

4
I. Company Profile
Zhejiang Shangyou Cutting Tools Co., Ltd. is currently the only professional manufacturer of high-precision and complex gear cutting tools in Zhejiang Province. It is located at No. 9, 25th Street, Eastern Industrial Park, Wenling City. Established in August 2004, the company mainly focuses on the research, development, production, and sales of high-speed gear hobbing cutters, gear shaping cutters, and gear shaving cutters. Its technology and product quality are at the leading level in the industry, with a high market share, representing the development level of China's gear hobbing, shaping, and shaving cutters.
The company was among the first in its industry to establish an ISO 9001 quality management system and has passed ISO 14001:2015 environmental management system certification. The company's standardized management and orderly operation adhere to sustainable development. Its sound R&D institution, excellent innovation capabilities, and strong brand awareness have earned the company numerous honors, including "Zhejiang High-tech Enterprise," "Zhejiang Specialized, Refined, and Innovative Small and Medium-sized Enterprise," and "Zhejiang High-tech Enterprise Research and Development Center." The company attaches importance to product quality innovation, increases investment in scientific research and hardware, and occupies the market with high-tech products. It has currently obtained more than 30 domestic patents and is a provincial patent demonstration enterprise.
The company possesses various types of sophisticated professional production equipment: imported advanced equipment such as the 6-axis fully CNC hobbing and grinding machine from Germany's SMS company, high-precision 3-axis CNC grinding wheel dressing machine; Sunnen internal honing machine from the United States; Taiwan CNC 5-axis linkage sharpening machine; nationally leading shaft and end face grinding machine; high-precision gear shaping cutter grinding machine from Germany's NILES; CNC gear shaping cutter grinding machine; Germany's Klingenberg P26, P65 gear testing equipment. Product processing and testing are carried out in a constant temperature environment to ensure the reliability and stability of product quality. The company can provide high-precision, high-tech, and high-performance non-standard complex cutting tools for the automotive, wind power, mining, heavy machinery, machine tool, shipbuilding, and railway vehicle industries.
5
II. Quality Philosophy
From its inception, the company has been committed to creating high-quality products, regarding product quality as the cornerstone of the company's survival and development. The company has successively passed the certifications of IS09001, IS014001, and OHSAS18001 management systems, various TLC product certifications, as well as safety production standardization and service certifications. It strictly adheres to this international quality management system, ensuring the quality of its products and facilitating the smooth implementation of the company's quality policy. To fundamentally strengthen quality management and improve the company's operational quality, the company uses the introduction of the excellent performance model as an opportunity to promote Total Quality Management, utilizing various quality statistical tools. Through internal audits, self-assessment, third-party audits or assessments, and QCC quality control circle activities, the company continuously seeks improvement opportunities and methods for continuous improvement, striving for excellent performance. Since its establishment, the company has never experienced any major quality complaints, and in annual inspections by various levels of quality supervision departments, the pass rate has always been 100%.
Table 1: Company Culture and Quality Culture
| Corporate Mission |
Realize corporate dreams, reflect employee value, benefit the public, and revitalize national industries. |
| Corporate Vision |
Build a century-old enterprise, keep pace with the times, and strive for excellence. |
| Core Values |
Be a person with a grateful heart, and do things with a sincere heart. |
| Quality Policy |
Integrity and law-abiding, excellent service, delivering quality products to customers. Pollution reduction and noise reduction, energy saving and consumption reduction, green contribution to society. |
| The integrated management policy is consistent with the company's business management policy, reflecting the company's quality, environmental, occupational health and safety management objectives and direction, including: compliance with national laws and regulations, meeting the quality, environmental, and occupational health and safety requirements stipulated in the contract; earnestly serving customers and society, enhancing their satisfaction, and establishing a good image for the company in the market; pursuing improvements in the management system and enhancing the level of system management; the company's top management should regularly review the integrated management policy and make necessary revisions. |
Table 2: Company Quality Objectives
| Process |
Quality Objective |
Target Value |
Calculation Method |
Statistical Period |
|
| COP1 |
Order Receiving and Review |
Order Review Timeliness Rate |
100% |
Order Review Timeliness |
Month + Year |
| COP2 |
Project Management |
On-time Completion of Product Design and Development Rate |
95% |
Number of tasks completed on schedule / Total number of tasks * 100% 务数*100% |
Annual |
| COP3 |
Product Manufacturing |
Production Plan Completion Rate |
90% |
Number of qualified products actually produced / Planned production number * 100% 产数*100% |
Month + Year |
| Defect Rate |
8.0% |
Defective products / Total number of products * 100% |
Month + Year |
||
| Scrap Rate |
3.0% |
Scrap quantity / Total quantity * 100% |
Month + Year |
||
| Shipment Plan Achievement Rate |
90% |
Actual shipment quantity / Planned shipment quantity *100% |
Month + Year |
||
| COP4 |
Product Delivery |
On-time Delivery Rate |
100% |
Number of on-time deliveries / Total number of deliveries * 100% |
Month + Year |
| COP5 |
Customer Feedback |
Number of Customer Complaints |
2 times/ Month |
Monthly Total |
Month + Year |
| SP1 |
Employee Satisfaction |
85% |
Employee Satisfaction Survey Scoring Method |
Half Year |
|
6
| Process |
Quality Objective |
Target Value |
Calculation Method |
Statistical Period |
|
| Human Resource Management 理 |
Employee Turnover Rate |
5.0% |
Number of employees who resigned this month / (Number of employees at the beginning of the month + Number of employees at the end of the month) / 2 初员工人数+当月月末员工 人数)/2 |
Month + Year |
|
| SP2 |
Infrastructure |
Annual Inspection Completion Rate of Special Equipment |
100% |
Actual number of verifications / Planned number of verifications * 100% |
Year |
| SP3 |
Process Operation Environment |
Number of Recurring Occurrences of Similar Issues in Process Environmental Inspections 重复发生次数 |
≤1 time |
/ |
Month + Year |
| SP4 |
Measurement Equipment Management 理 |
Calibration and Verification Plan Completion Rate |
100% |
Actual number of calibrated and verified items / Planned number of items * 100% |
Annual |
| SP5 |
Laboratory Management |
Test Completion Rate |
100% |
Actual number completed / Planned number * 100% |
Month + Year |
| SP6 |
Knowledge Management |
Knowledge Submission Plan Completion Rate |
90.0% |
Actual number of knowledge submissions / Planned number |
Half Year |
| SP7 |
Capability and Awareness |
Training Plan Completion Rate |
100% |
Actual number of training sessions / Planned number of training sessions * 100% |
Month + Year |
| SP8 |
Documented Information |
Document Distribution and Recovery Rate |
100% |
Number of documents recovered / Number of documents distributed x 100% |
Month + Year |
| SP9 |
Supplier Management |
Supplier Performance Evaluation Score A Grade Ratio |
80% |
Number of Grade A suppliers / Total Number of Suppliers |
Month + Year |
| SP10 |
Procurement Management |
Supplier Delivery Punctuality Rate |
100% |
Number of on-time deliveries / Total number of deliveries * 100% |
Month + Year |
| Supplier Batch Qualification Rate |
97% |
Number of qualified batches / Total number of procurement batches *100% |
Month + Year |
||
| Supplier Arrival Rate |
95% |
Actual arrival quantity / Planned arrival quantity Quantity |
Month + Year |
||
| SP11 |
Equipment Management |
Equipment Maintenance Plan Completion Rate |
100% |
Actual maintenance quantity / Planned maintenance quantity * 100% |
Month + Year |
| OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) |
80% |
Availability x Performance x Yield Rate |
|||
| SP12 |
Tooling and Die Management 理 |
Die Failure Rate |
5% |
Actual number of die failures / Total number of dies *100% |
Month + Year |
| SP13 |
Gauge Management |
Gauge Calibration Plan Completion Rate |
95% |
Actual number of calibrations / Planned number of calibrations * 100% |
Year |
| SP14 |
Identification and Traceability Traceability |
Product Identification Spot Check Compliance Rate |
95% |
Number of correct spot checks / Total number of spot check inspection procedures x 100% |
Quarter |
| SP15 |
External Property |
External Property Loss Rate |
5% |
Number of losses / Total number of customer properties |
Quarter |
| SP16 |
Protection Management |
Inventory Turnover Rate |
15% |
Sales / Inventory product and material value x 100% |
Month + Year |
| Warehouse Accounting Accuracy Rate |
100% |
/ |
Quarter |
||
| SP17 |
Change Management |
Number of Change Risk Occurrences |
1 time / Month |
Actual number of risks occurred |
Month + Year |
| SP18 |
Products and Services Release |
Finished Product Spot Check Qualification Rate |
98% |
Number of qualified spot checks / Total number of spot checked products *100% |
Month + Year |
| Number of Factory Inspection Misses |
≤2 times |
Number of Factory Inspection Misses |
Month + Year |
||
7
| Process |
Quality Objective |
Target Value |
Calculation Method |
Statistical Period |
|
| SP19 |
Nonconformance Control |
Comprehensive Finished Product Rate |
97% |
Number of finished products / Number of input materials x 100% |
Month + Year |
| SP20 |
Customer Satisfaction Measurement |
Total Customer Satisfaction Score |
90% |
Survey form, comprehensive evaluation of delivery performance Method |
Annual |
| SP21 |
Nonconformity Correction Measures |
Number of Recurring Problems |
≤2 times |
Number of Recurring Problems |
Quarter |
| MP1 |
Organizational Environment and Stakeholder Needs |
Number of stakeholder customer risk occurrences Number |
≤3 times |
Actual number of stakeholder customer risk occurrences Number |
Annual |
| MP2 |
Risk and Prevention Management |
Number of Major Risks Occurred |
≤1 time |
Number of Major Risks Occurred |
Annual |
| MP3 |
Performance Analysis and Evaluation |
Number of times the substandard target has been repeated Number of times |
≤1 time |
Number of times the substandard target has been repeated |
Month + Year |
| MP4 |
Internal Audit |
Internal Audit Plan Completion Timeliness Rate |
100% |
Audit completion time / Planned completion time x 100% |
Year |
| MP5 |
Management Review |
Management Review Punctuality Rate |
100% |
Actual / Planned |
Annual |
| MP6 |
Quality Cost |
Defective Quality Cost Rate |
1.9% |
(Internal losses + external losses) / Sales Sales |
Month + Year |
| MP7 |
Continuous Improvement |
Continuous Improvement Target Achievement Rate |
95% |
Number of improvement projects implemented / Number of planned improvement projects per year x 100% |
Quarter |
8
III. Enterprise Quality Management
(I) Quality Management Organization
With a high degree of emphasis on product quality, the company has established a quality manager system and formulated inspection standards for various materials, components, and products. Each department performs its duties, communicates and coordinates with each other, and strengthens product quality control throughout the R&D, procurement, and production processes.
Integrated management policy for quality/environment/occupational health and safety:
a. The company establishes an integrated management policy for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, ensuring that the policy aligns with the organization's objectives;
b. This includes a commitment to meeting customer and regulatory requirements and continuously improving the effectiveness of the quality management system;
c. Provides a framework for setting and reviewing integrated management objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety;
d. Top management must communicate, disseminate, and ensure understanding and implementation of the integrated management policy for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety within the organization through training and communication, to achieve the ultimate goal of the policy;
e. The company reviews and revises the suitability of the integrated management policy for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety through management review to adapt to changes in the internal and external environment;
f. The integrated management policy for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety must be documented, approved by the general manager, and implemented;
Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities of the Organization
Top management determines the company's organizational structure, clarifies responsibilities and authorities, and implements internal communication.
Responsibilities and Authorities
1) The company defines the responsibilities and authorities of each functional department and their interrelationships, and communicates, guides, and controls the coordination of activities related to quality, environment, and occupational health and safety within the company organization to promote effective integrated management of quality, environment, and occupational health and safety;
2) The company's integrated management system (IMS) structure, responsibilities, authorities, and interrelationships are shown in the organizational chart.
3) The responsibilities and authorities of personnel in various departments and their interrelationships are shown in the "Departmental Position (Responsibilities) Description" and "Individual Job Responsibilities"; the company achieves communication through the release of the "Management Manual" and "Individual Job Responsibilities" documents, enabling all employees to clearly understand their responsibilities, participate fully, and effectively carry out various activities.
General Manager
1) Based on national policies, laws and regulations, and market development trends, comprehensively plan the company's and product's development direction;
2) Establish the company's integrated management policy and objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction, ensuring attention to customer requirements, and clarifying the direction for company development;
3) Plan, establish, and implement an integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety using the "process approach," and continuously improve its effectiveness to meet the requirements of the objectives;
9
4) Determine the company's organizational structure, clarify the responsibilities and authorities of each department, and ensure internal communication;
5) Ensure the provision of necessary resources for the establishment, implementation, and improvement of the integrated management system, creating a work environment that enables all employees to fully participate in achieving the integrated management objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, giving full play to employee initiative and talent to bring maximum benefits to the company;
6) Appoint a management representative, determine their responsibilities and authorities, and provide support to ensure the establishment, implementation, and maintenance of the integrated management system process;
7) Pay attention to customer satisfaction, examine the performance of the quality management system, preside over management reviews, review the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the quality management system, and continuously improve it to achieve the company's established goals;
8) Take full responsibility for the quality of the company's products.
Management Representative
1) In accordance with the requirements of the company's integrated management policy and objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, cooperate with the general manager to plan the integrated management system, ensuring that the processes of the integrated management system are established, implemented, and maintained;
2) Report to the general manager on the achievements made in the integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, and propose the needs for improvement of the integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, contributing to the improvement of system processes;
3) Enable all employees throughout the company to recognize that the company depends on customers, and that meeting customer requirements is crucial to the company's fate—a quality awareness.
4) Responsible for the liaison and communication with external parties, including customers, regarding the company's integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety;
5) Responsible for organizing the preparation of the management manual and procedural documents; develop a management review plan, organize management reviews, supervise the implementation of review resolutions, and conduct follow-up verification and reporting; responsible for reviewing the "Management Manual" and approving procedural documents.
Shared Responsibilities of Department Heads
1) Implement the company's integrated management policy for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, achieve the department's integrated management objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, and contribute to the achievement of the company's integrated management objectives for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety;
2) Implement the resolutions/instructions of the general manager, supervisor, and management review meeting regarding quality, environment, and occupational health and safety work, and preside over various integrated management work for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety in the department;
3) Determine the establishment of departmental positions and responsibilities, implement and improve the departmental responsibility system to ensure that the department's work proceeds in an orderly manner;
4) Develop "_Departmental Position (Job) Description" and "_Departmental Individual Job Responsibilities," determine the on-the-job ability requirements for various positions in the department, conduct assessments and evaluations of personnel in various positions, and provide training to ensure that personnel in various positions have continuous competence;
5) Collect and analyze information/data related to the department, evaluate improvement needs, and implement continuous improvement;
6) Participate in relevant integrated management analysis meetings for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety.
7) Participate in management reviews, report on the performance and improvement suggestions of the department's integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety, and contribute ideas for system improvement;
Technical Department Manager
1) Responsible for product realization planning, preparation of quality plans for special products, projects, and contracts, and responsible for the quality of special products, projects, and contracts;
2) Responsible for the centralized management of design and development, and responsible for the quality of design and development (compliance with hygiene and safety regulations, meeting customer needs and standards);
3) Responsible for the control and centralized management of design and development output drawings and documents, and responsible for the adequacy, suitability, and effectiveness of the distribution of drawings and documents;
4) Responsible for the application research and adoption of new materials and technologies, improving the company's technical level and product quality;
5) Manage drawings and/or samples provided by customers and protect customer property;
6) Cooperate with the production department to solve major technical quality problems;
7) Responsible for the control of management system documents and records required by the integrated management system for quality, environment, and occupational health and safety;
8) Responsible for the implementation and control management of product status identification;
9) Responsible for the control and management of monitoring and measuring equipment;
10) Cooperate with senior management in the planning of company-required measurement analysis and improvement processes;
11) Monitor and measure processes, propose improvement measures to enhance process capabilities, and implement tracking of their effectiveness;
12) Responsible for the formulation of inspection standards for the entire process of product incoming inspection, product realization (including trial production and mass production), and finished products, and for the monitoring and measurement of products, ensuring the conformity of transferred, released, and factory products;
13) Responsible for the identification and review of nonconforming products, supervise and track the handling of nonconforming products, and responsible for the reinspection of reworked products and the statistics of quality indicators;
14) Responsible for determining, collecting, and analyzing data from monitoring and measurement, evaluating improvement needs, organizing corrective/preventive/improvement measures, tracking and verifying effectiveness, and being responsible for the effectiveness of continuous improvement;
Production Department Manager
1) Oversee the management of materials and finished products in the material warehouse and finished product warehouse;
2) Responsible for reviewing product delivery dates in sales contracts, formulating production plans and material procurement plans, ensuring smooth production and logistics, and being responsible for the timely completion of production plans and on-time delivery;
3) Responsible for the safety of stored materials in material/finished product warehouses, and for the proper labeling and protection of stored materials;
4) Responsible for formulating relevant internal warehouse management regulations;
5) Regularly inventory stored materials to ensure consistency of warehouse items' accounts, physical inventory, and cards;
6) Load and ship products according to customer requirements, and be responsible for contacting customers and monitoring and measuring customer satisfaction.
7) Responsible for the centralized management of the company's raw materials, components procurement, and outsourcing processes, conducting supplier assessments and reassessments, and being responsible for the quality and timeliness of incoming raw materials, components, and outsourced parts;
8) Implement the "mutually beneficial relationship with suppliers" quality/environmental/occupational health and safety integrated management principles, actively collect market information on procurement and outsourcing materials, investigate and research new suppliers, develop suppliers with the best price-performance ratio, and strive to reduce product quality costs;
Administrative Department Manager
1) Responsible for the centralized management of the company's human resources, and responsible for the adequacy, suitability, and job competency of the human resources provided;
2) Cooperate with top management in planning the organizational structure and responsibilities, prepare the company's organizational chart and "Company Position (Job) Description," and organize various departments to prepare "Department Responsibilities, Individual Job Responsibilities" as the basis for on-the-job personnel assessment and recruitment;
10
3) Based on the needs of departmental personnel, propose departmental personnel allocation plans (including personnel appointments and removals), the construction of cadres and technical talent teams, and achieve optimal personnel allocation;
4) Based on the company's situation, organize the formulation of company recruitment management regulations, employee handbooks, annual training plans, training regulations, departmental functions, and job descriptions, and organize their implementation.
5) Responsible for the planning and implementation of company-wide training, responsible for training effectiveness, and responsible for recruitment effectiveness;
6) Develop recruitment plans and procedures, develop and introduce external talent, organize and implement recruitment work, and participate in the interview and screening of applicants;
7) Establish an internal communication mechanism within the company, understand employee dynamics in a timely manner, control personnel turnover rates; coordinate/resolve labor relations disputes.
8) Based on the company's development strategy, formulate scientific and feasible departmental work plans and implement them.
9) Draft investment documents, project approval, construction, and reporting for engineering projects;
10) Coordinate the company's vehicles, security, logistics, and canteen management, organize the formulation of scientific and reasonable management regulations, and implement them;
11) Coordinate the company's safety and fire protection work, employee social security, and work injury handling;
12) Responsible for the configuration, maintenance, and management of factory buildings, warehouses, and related facilities;
13) Responsible for the configuration, maintenance, and management of communication and information systems;
14) Responsible for the company's "three-in-one" management system audit work;
15) Responsible for the management of other company office affairs.
Workshop Directors
1) Responsible for the centralized management of personnel, machines, materials, methods, environment, and production operations in the workshop, achieving the integrated management goals of quality/environment/occupational health and safety in the workshop;
2) Execute production instructions from the production manager, organize the production of the workshop, strive to complete the production plan, and ensure product quality and delivery schedule;
3) Coordinate the product flow between various processes in the workshop, strive to achieve balanced production in each process, and perform production scheduling within the workshop;
4) Supervise operators in carrying out daily maintenance and maintenance of equipment and tooling;
5) Responsible for the control and management of the workshop's working environment, ensuring civilized and safe production;
6) Guide operators to operate strictly according to standards/drawings/processes/operating instructions, and make corresponding records to ensure product quality conformity;
7) Responsible for the labeling and traceability of processed products in the workshop, protecting inspection status labels, and protecting the property of customers in the workshop;
11
8) Handle product handling, packaging, and labeling protection according to regulations;
9) Guide employees in the correct use of monitoring and measuring equipment to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness;
10) Supervise operators in performing process self-inspection and cooperate with inspectors in performing inspections;
11) Handle the isolation, rework, repair, and scrapping of nonconforming products;
12) Responsible for the collection, statistical analysis, evaluation of improvement needs, and implementation of improvements for relevant data in the workshop;
Internal Auditor
1) Strictly in accordance with relevant laws, regulations, standards, and quality documents, conduct quality/environmental/occupational health and safety integrated management system audits according to company arrangements and in combination with the company's actual situation;
2) Collect and analyze relevant documents and materials, prepare audit checklists, prepare for the audit, and conduct on-site audits; eliminate interference during the audit, go all out, and be faithful to the audit objectives;
3) Manage relationships both inside and outside the audit group to achieve optimal audit results;
4) Respect objective facts, ensure the impartiality of the audit work, truthfully record the status quo of the audited department during the audit process, and write non-conformance reports;
5) Based on objective evidence, write objective, fair, and factual audit reports, propose the need for corrective measures, and verify their implementation effectiveness;
Inspector
1) Implement the company's integrated management policy for quality/environment/occupational health and safety, and diligently complete various inspection responsibilities stipulated in the management manual and procedural documents;
2) Strictly follow the requirements of relevant acceptance standards, inspection specifications, and drawings, independently exercise inspection powers, identify and record product quality, and ensure quality control;
3) Properly label the inspection status of products and record non-conforming items;
4) Carefully fill out quality records, organize, analyze, and feedback quality information;
5) Responsible for the rework, initial evaluation, and disposal of non-conforming products;
6) Receive training and continuously improve business capabilities;
Tester
1) Responsible for conducting functional testing of raw materials, outsourced parts, processed products, and finished products;
2) Responsible for comprehensive functional testing and evaluation of outsourced materials, new raw material samples, and new products;
13
3) Issue test reports and take responsibility for the accuracy of the data;
4) Responsible for the weekly inspection of testing instruments to ensure their accuracy;
5) Receive training on relevant national regulations and professional knowledge to improve personal quality.
(II) Quality Management System
Since the introduction of the quality management system, the company has adhered to the company's integrated management policy for quality/environment/occupational health and safety of "integrity and law-abiding, excellent service, fine products delivered to customers; pollution reduction, noise reduction, energy saving and consumption reduction, green contribution to society." Based on the requirements of the quality management system, a quality management system has been established around the design, development, production, and sales processes of gear hobs, forming a quality manual, procedural documents, and other quality documents, which are implemented, maintained, and continuously improved for effectiveness.
1. Quality Management System Policy and Objectives
The company's quality policy is: Integrity and law-abiding, excellent service, fine products delivered to customers
Pollution reduction and noise reduction, energy saving and consumption reduction, green contribution to society.
Figure 1 Diagram of the company's management system operation process
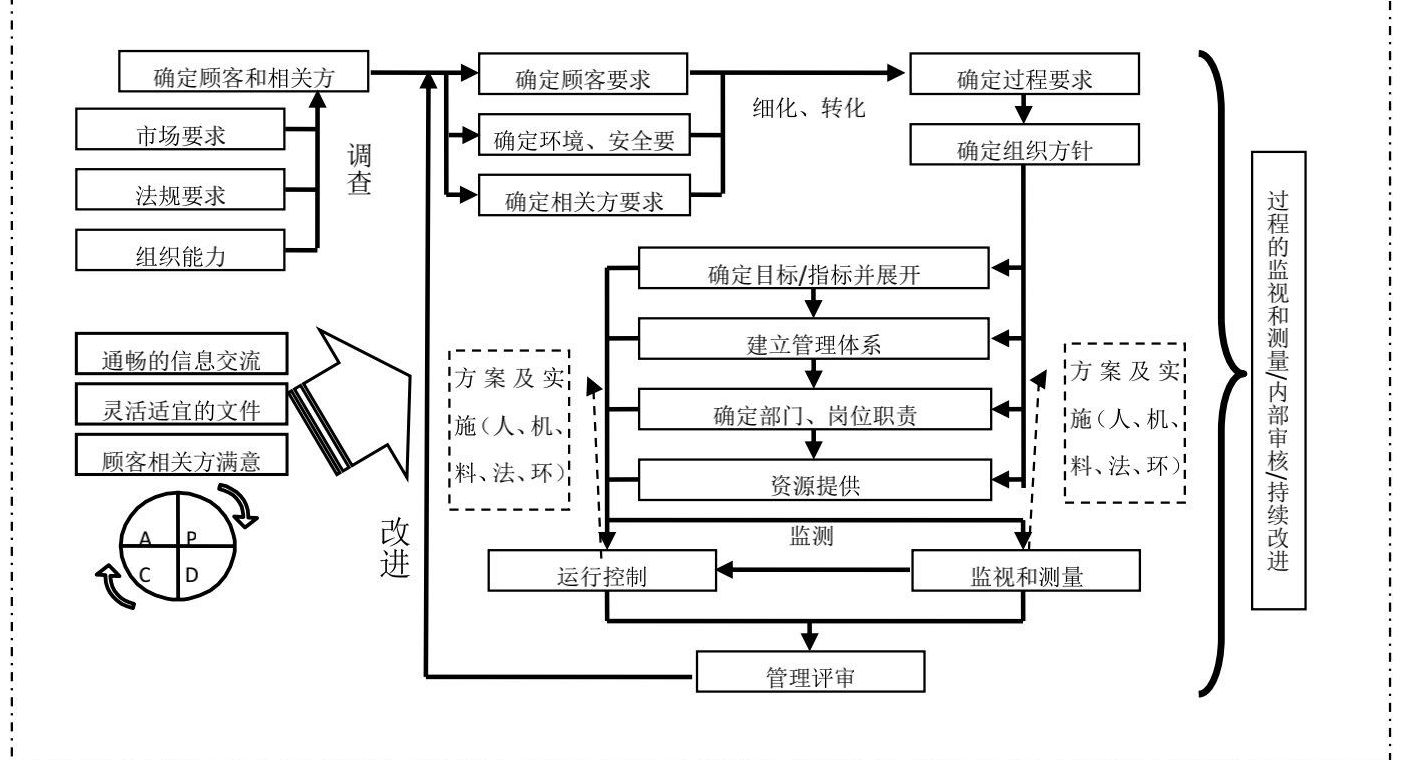
Company Quality Objectives:
① Customer inspection acceptance rate of 91% or higher;
② Product delivery timeliness rate of 95% or higher;
③ Customer satisfaction rate of 98% or higher.
12
Company Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety Objectives:
① Noise emission meets standards;
② 100% classified collection and treatment of production and living waste;
③ Zero incidence of occupational diseases;
14
④ Prevention of work-related injuries and fire accidents.
To achieve the company's quality and safety responsibility objectives, the company has established a sound quality and safety leadership organization, establishing a product quality and safety leadership committee headed by the general manager. Sub-committees are set up in various centers and functional departments to be responsible for the supervision and assessment of product quality and safety work.
The company has established an integrated comprehensive quality management system with strategy as its core and the GB/T19580 Excellent Performance Model as its framework, meeting the requirements of six major stakeholders: customers, shareholders, employees, suppliers, society, and partners. Corresponding strategic planning and quality objectives have been established at all levels of the company, and a quality assessment KPI and quality accountability system have been established based on the company's performance assessment system.
2. Quality Education
During the operation of the system, the company uses various scientific and effective methods for measurement, analysis, and improvement, based on the PDCA system method for continuous improvement. The company uses various tools to improve the performance of various departments and levels, and adopts benchmarking and learning methods to continuously correct individual work ideas and methods to ensure the achievement of individual and overall company goals. The company actively communicates and exchanges with external parties and invites experts to provide specialized training to company employees as needed. The company regularly conducts quality education for employees at all levels, and conducts specialized management of quality control points to ensure the consistency of product quality in the manufacturing process.
To firmly establish the integrity awareness of all employees, the company formulates an annual quality integrity education and training plan at the beginning of each year, implementing three-level quality integrity education and training. Department heads, according to company requirements, prepare education and training plans and content, and carefully organize the education and training of their subordinates. Workshop directors are responsible for the integrity publicity and education work of team leaders and employees. The company uses a variety of methods to implement quality integrity education for employees, including thematic training, posting or conveying written materials, exchange of experience of advanced employees in quality integrity, use of morning meetings or pre-shift meetings, and use of image displays. The company provides certain rewards to personnel who achieve excellent results in quality integrity education and training, and at the same time promotes and popularizes experience among employees. Employees who do not participate in quality integrity education and training on time or who fail the training assessment will be subject to certain penalties.
3. Quality Regulations and Responsibility System
The company collects laws, regulations, and other standards and requirements, and formulates relevant internal standards to ensure that products meet the requirements of national laws, regulations, and national and industry standards (some product indicators exceed external requirements), practicing social responsibility through product technology. At the same time, the company has formulated "Quality Reward and Punishment Management Standards", "Quality Assessment Management Measures", etc., to punish product quality problems, and follows the principle of not letting go of quality accidents.
Table 3 Quality standards and other relevant laws observed by the company
| Category |
Content |
| Company standardized governance |
"Company Law", "Enterprise State-owned Assets Management Measures", "Accounting Law", "Accounting Standards", "Financial Regulations" etc. |
| Protecting employee rights and Social responsibility |
"Safety Production License Regulations", "Special Equipment Safety Supervision Regulations", "Dangerous Chemical Safety Management Regulations", "Production Safety Accident Reporting and Investigation and Handling Regulations" etc. |
| Implementation of product standards and formulation/market access |
GBT 6083-2016 "Gear Hobs - Basic Types and Dimensions" GBT 6084-2016 "Gear Hobs - General Technical Conditions" ISO 4468-2009.MOD ISO 2490:2007 |
15
| Category |
Content |
| Internal and External Audit Mechanisms |
The company has established institutions such as a supervisory board and an internal audit department, and has signed a long-term audit cooperation agreement with Wenling Zhonghe United Certified Public Accountants Firm This has perfected an independent internal and external audit mechanism. |
The company has formulated "Internal Audit Management Procedures" and "Management Review Control Procedures," and has cultivated an internal audit team. To ensure the effectiveness and continuous improvement of the system's operation, system audits, process audits, product audits, and quality inspections are arranged. For nonconformities found during audits, the responsible department analyzes the causes, formulates corrective or preventive measures, implements rectification, and verifies the rectification effect. Finally, an internal audit report is generated, providing suggestions for system rectification and the prevention of nonconformities. This report serves as an important input for management review and is reported to the highest management level.
The company has formulated "Nonconforming Product Control Procedures," "Corrective and Preventive Action Management Procedures," and "Logistics Sampling Management Specifications" to strictly control nonconforming products. All company products undergo online inspection before being allowed to proceed to the next process or leave the factory. Any nonconforming products have clear requirements for identification, recording, isolation, and handling. All reworked or repaired nonconforming products must pass re-inspection before proceeding to the next process.
Meanwhile, according to the "Product Monitoring and Measurement Control Procedures," detailed records are kept for all nonconformities. A designated person performs statistical analysis, and the responsible unit formulates corrective and preventive measures based on the "Corrective and Preventive Action Management Procedures" and implements rectification. The problem item can only be closed after the effectiveness of the corrective and preventive measures has been evaluated.
In addition, the company has also formulated systems such as the "Quality Manual," "Supplier Control Procedures," and "Employee Training Management Measures." Accountability is enforced for quality issues, employees receive education, and systematic approaches are emphasized in daily R&D and production operations. Activities such as quality control circles and continuous improvement, along with the application of quality tools, fully utilize the PDCA cycle for continuous improvement and the pursuit of excellence.
(3) Quality and Safety Risk Management
To achieve the company's quality and safety responsibility goals, the company has established a sound quality and safety leadership organization. A product quality and safety leadership committee, chaired by the chairman of the board, has been established to oversee and evaluate product quality and safety work. In 2024, a "Chief Quality Officer (CQO)" system was established, clarifying the CQO's responsibilities and rights, and fully exercising the quality and safety "veto power." The Quality Department signs "Product Quality and Safety Responsibility Letters" with various departments, further implementing them at each position and conducting assessments.
Quality and safety knowledge is disseminated through the annual "Quality Month" activities in September to strengthen employees' awareness of quality and safety. Through the quality, environmental, and occupational health and safety management system audits, quality and safety hazards are promptly identified and eliminated.
During the design, production, and assembly processes, the following measures are mainly adopted to ensure quality and safety:
The design department conducts FEMA analysis and error-proofing design; the quality department strictly implements the "four inspections" system of initial inspection, patrol inspection, final inspection, and supervisory inspection;
| Project |
Content |
|
| Detection System |
Quality department personnel, production department personnel, and material preparation personnel are responsible for the detection and reporting of product quality issues during production work; purchasing department personnel are responsible for the detection and reporting of product quality incidents during finished product storage and loading and unloading. |
|
| Early Warning System |
The quality department, production department, and purchasing department, in accordance with their respective responsibilities, strengthen the detection and analysis of quality incidents, improve quality awareness and risk awareness, promptly analyze the feasibility of product use, and identify trends in problems, making timely warnings and ensuring the effective operation of the production system. |
|
| Emergency Response |
Major |
(1) The quality department organizes relevant departments to analyze the causes of the problem and, based on the impact of the incident, formulates corresponding emergency measures, including aspects such as product handling, impact elimination, and loss reduction; (2) Each department is responsible for promptly organizing relevant work according to the requirements of the emergency measures; (3) The quality department is responsible for inspecting the implementation of the emergency measures. |
| Significant |
(1) After a significant quality incident occurs, the quality department is responsible for promptly notifying relevant personnel to control the problematic products, and the purchasing department is responsible for isolating and identifying the same batch of problematic products or products that may have problems to prevent further circulation or shipment. (2) The quality department organizes relevant departments to analyze the causes, and the technology department provides corresponding technical support and gives processing opinions; (3) The production department is responsible for verifying the effectiveness of the measures. |
|
| General |
(1) The production department is responsible for promptly reporting the problem to the production department; (2) The production department analyzes the cause of the problem, formulates corresponding improvement measures, and implements them specifically; (3) The quality department/sales department verifies the rectification effect according to the corresponding situation. |
|
| Potential |
(1) Based on the principle of prevention first, potential quality incidents must be given high attention. Once a potential incident occurs, the quality department must be notified immediately, and the quality department will organize relevant personnel to assess the impact and hazard level of the potential quality problem; (2) Based on the results, formulate corresponding remedial measures and preventive measures to prevent quality accidents and reduce losses; (3) The quality department is responsible for verifying the effectiveness of preventive measures. If necessary, products need to be supplied from a designated point to facilitate timely and effective control of any spread. |
|
| Emergency Handling |
Product handling is the responsibility of the department where the problem occurred. After the problem occurs, the product should be quickly isolated and correctly identified. Before the final disposal of the product is issued, no one may dispose of the product arbitrarily; for products that need to be recalled, the quality department is responsible for recalling them, and after recall, they should be promptly isolated and identified. |
|
Table 4 Quality and Safety Emergency Plan
The company has formulated a quality and safety emergency plan and established an emergency leadership team with the general manager as the team leader, the quality authorized person and the executive deputy general manager as deputy team leaders, and the quality department, purchasing department, technology department, sales department, and finance department as members. The responsibilities of the emergency leadership team and each relevant department have been clearly defined.
The process department conducts process discipline checks on key processes every month;
16
Production manufacturing departments implement a manager responsibility system to track and supervise the entire production process;
Establish the concept of "quality is produced," where employees inspect their own products according to the drawings, determine whether they are qualified, and make relevant self-inspection records on the "Self-Inspection Form";
The modularized production model exposes and controls key quality aspects of the product, thus ensuring product quality and safety and preventing quality and safety risks.
17
IV. Quality Integrity Operation Management
(I) Quality Commitment
1. Requirements that the enterprise must comply with as clearly stipulated by laws, regulations, and standards related to the enterprise or product
During operation, the company shall operate and implement standardized governance in accordance with the Company Law, Accounting Law, Contract Law, Product Quality Law, Accounting Standards, Enterprise Income Tax Law, etc., and protect employee rights and social responsibilities in accordance with the Labor Law, Trade Union Law, Consumer Rights Protection Law, Environmental Protection Law, Safety Production Law, Occupational Disease Prevention and Control Law, ISO14001 standard, etc.
Products must be implemented according to:
GBT 6083-2016 "Gear Hobs - Basic Types and Dimensions"
GBT 6084-2016 "Gear Hobs - General Technical Conditions"
2. Integrity and Law Abidance
Senior leaders follow the management philosophy of "legal operation and integrity operation," strictly abide by the Company Law, Economic Law, Contract Law, Product Quality Law, Safety Production Law, Environmental Protection Law, Labor Law, and relevant laws and regulations of the machinery industry, strengthen employee legal knowledge training, cooperate with government departments to carry out legal education activities, encourage and commend employees' "positive energy," so that the style of integrity and law abidance is deeply rooted in the consciousness and behavior of all employees of the company. The company's contract default rate is zero, bank loans are never overdue, overdue receivables are reduced to a reasonable range, senior and middle-level leaders of the company have no records of violations of laws and disciplines, the number of employee violations is zero, and a good credit and moral image has been established among customers, users, the public, and society.
Figure 2 Various explicit commitments made by the enterprise in its public statements
Hob Series
Gear Shaper Cutter Series

18
2. Meeting Customer Needs
The company attaches great importance to technological research and development, strengthens investment in research and development, takes customer needs as the center, actively listens to customer opinions and suggestions on functions, quality, and configuration, carries out product improvement and innovation activities, and meets customer needs for products and delivery times. In terms of product quality, the company strictly implements the quality management system and ensures product quality and safety through technological breakthroughs, quality improvement, and QC group activities.
(II) Operation Management
The company identifies integrity factors throughout the management process, establishes an evaluation table, and develops control measures.
Table 5 Integrity Factor Analysis and Control Measures Table
| Serial Number |
Process Name |
Factor Category |
Integrity Factor Score Analysis |
Breach of Trust Performance |
Consequences of Breach of Trust |
Control Measures |
Breach of Trust Risk Assessment Analysis |
Is it a major breach of trust factor? |
|
| Possible Nature |
General Nature |
||||||||
| 1 |
Design and Development Planning (Project Review, Project Plan Preparation, Design and Development Input) |
Personnel Structure |
Employees need to keep confidential |
Leakage of formulas, etc. core confidential information |
Company confidential information leakage |
Employees sign confidentiality agreement |
Very few |
General |
No |
| Employees need to Need to be honest and trustworthy |
Conceal personal and work situation |
Employee integrity Insufficient |
Employees Sign an agreement |
Very few |
General |
No |
|||
| Whether it has market research capabilities |
Distorted research information |
Design planning is not correct |
Training |
Very few |
General |
No |
|||
| Confirmed project The person in charge's business quality is not strong |
R&D is not going smoothly Favorable |
Project progress slow, poor quality |
Training, examination Verification |
Very few |
General |
No |
|||
| Environmental facilities |
Whether it has various professional equipment |
It is unclear whether it has various professional equipment (at the beginning of the project, the company may decide to use equipment that is not very suitable for the project test) |
Product R&D cannot be carried out smoothly |
Establish equipment management archives |
Very few |
General |
No |
||
| The company lacks integrity atmosphere |
Work situation reflection Not true |
Employee integrity Poor |
Build integrity Corporate culture |
Very few |
General |
No |
|||
| System implementation |
Whether to timely absorb relevant standards issued by the state Collection |
Failure to understand and utilize the newly distributed national standards |
Use of illegal raw materials, or the amount added does not meet the requirements; the product is not qualified |
Timely acquisition and update of relevant laws, regulations, and national standards |
Impossible |
Serious |
No |
||
| Whether the selected raw materials meet national regulations and standards standards |
Does not meet national regulations and standards |
Use of illegal materials |
Timely acquisition and update of relevant laws, regulations, and national standards |
Impossible |
Serious |
No |
|||
| Product development Relevant regulations |
Failure to follow regulations Work |
The project cannot be completed on time with guaranteed quality Completed |
Training, examination Verification |
Very few |
General |
No |
|||
1. Product design integrity management
The company's product design and R&D strictly follow the "Design and Development Control Procedure", from R&D project establishment, various activity records during the process, R&D process summary, to management evaluation, controlling the entire process related to R&D.
2. Raw material or component procurement integrity management
The company classifies materials into three categories (A, B, and C) based on the risk level of the materials to product quality. For Category A material suppliers, in addition to meeting the legally required qualifications, regular on-site audits are also required. For Category B material suppliers, the company must first conduct a risk analysis of the material and decide whether an on-site audit is needed based on the quality of the material provided by the supplier. For Category C material suppliers, generally only the qualifications are audited. After the company conducts qualification audits and on-site audits of material suppliers, material suppliers that meet the requirements and are approved for procurement should establish quality files. All batches of purchased raw materials are subject to full inspection; any raw materials that do not meet the specified standards are not allowed to be stored or used.
Regarding equipment and component procurement, the relevant qualifications of suppliers are strictly reviewed. When procuring equipment and components, standard parts are purchased and used whenever possible; for parts requiring special processing, the effect of use must be fully verified to ensure that they meet the company's requirements. All equipment must undergo equipment verification before use to ensure that it meets product process requirements.
3. Production process integrity management
The company's production department and technology department are specifically responsible for the production management and technology management of various products. Various production management systems, work standards, job operating procedures, and various process procedures, management procedures, and standard operating procedures have been formulated and gradually improved. On-site training in the workshop and pre-shift and post-shift meetings are used to provide comprehensive job skills training for operators at various positions, requiring certification before taking up their posts. Various methods are used for supervision and assessment to enhance employees' quality awareness and improve operational skills. During the production process, managers at all levels strictly fulfill their management responsibilities, conduct timely inspections, and promptly correct errors to ensure stable production order.
Before adding materials, the raw materials, auxiliary materials, and packaging materials required for production are reviewed to ensure the quality of intermediate products and finished products. The "three no" principle of "no production, no acceptance, no transfer" for non-conforming products is strictly implemented. Quality control points are set for key processes to urge employees to conduct self-inspection and mutual inspection, implement monitoring and verification procedures, and strictly manage batch number records, ensuring that receipt, issuance, and verification are unified. Material balance is performed for each production step to ensure that the input of materials and the output of products are consistent with the planned requirements, confirming that there are no potential quality hazards.
Production records are reviewed, printed, and kept by the production department. Employees must fill out production records promptly as required, ensuring that the handwriting is clear, the content is true, the data is complete, and the operator and reviewer sign for confirmation. After each batch of production is completed, the workshop statistician summarizes and reviews the records, promptly submits them to the production department, and after review and confirmation, organizes and files them by batch number, managed by a designated person.
19
Based on industry characteristics and actual conditions, the company strengthens the level of information construction in the production process, uses the production management module of the ERP system to collect and monitor the entire process, implements systematic management of the company's entire production process, taps internal potential, leverages the strength of technical backbone personnel, conducts continuous improvement or technological innovation work on existing equipment, establishes a technical task force to tackle weak links; production employees must undergo training and assessment before taking up their posts, establish personnel training files, and conduct training through various methods such as centralized training, pre-shift meetings, "passing on, helping, and guiding," and visualization to strengthen their work skills and quality awareness. Production employees strictly abide by workshop discipline.
The company implements a refined production organization model to shorten the production and delivery cycle, quickly adapt to the fluctuations in the variety and quantity of market orders, meet customer needs while reducing inventory, meet customers' comprehensive understanding of the performance of pneumatic braking systems and further recognition of product quality, increase order rates, and largely solve after-sales quality problems, reduce the workload of after-sales service personnel, and make after-sales service arrangements more flexible.
(5) Marketing Management
According to strategic requirements, the company segments the market to improve the effectiveness and targeting of resources and operations. The company divides customers into direct customers and indirect customers. It determines the needs and expectations of different types of customers, determines appropriate methods based on their needs and expectations, establishes corresponding systems and teams, establishes various channels and methods, and specifically understands customer needs and expectations.
Table 6 Identifying Customer Needs and Expectations to Implement Differentiated Marketing Strategies
| Importance |
Characteristics/Needs |
| Strategic Customers |
Form strategic partnerships, key customers to develop and maintain, large purchase volume and amount, stable purchase frequency, High product quality requirements |
| Important Customers |
Relatively important customers, larger purchase volume and amount, stable procurement, high requirements for quality and timely delivery |
| General Customers |
Small purchase volume and amount, unstable frequency, price-sensitive, low loyalty |
The company uses channels such as exhibitions, industry conferences, industry standard committees, public media, the Internet, and external organizations, and methods such as questionnaires, face-to-face or telephone interviews, observation inquiries, and external commissioning to understand customer needs and expectations.
Various departments of the company regularly collect customer information, analyze it, and classify and summarize the determined customer needs information according to different market segments to form a database of needs and expectations for different customer groups. Summary materials on the overall needs characteristics of different segmented market customer groups are derived from this and used for reference in decision-making for product planning, product development and design, and process control.
The company upholds a service tenet of "Professionalism, Passion, Thoughtfulness, and Timeliness." Through publicity and training, all levels of personnel understand and consistently implement this service tenet.
20
The company advocates a corporate spirit of "Challenging the Future, Pursuing Excellence," relying on technological development and striving for growth through optimal service. Our tenet for technical support and service is "Professionalism, Passion, Thoughtfulness, and Timeliness." Our service principles are "Customer First, Service First, High-Quality Service, and Timely Response." The quality and efficiency of our service
Timeliness is crucial to the company's positive image in the eyes of customers and its future development. Therefore, we aim to provide customers with superior products and services, thereby enhancing customer recognition and improving the company's reputation and brand awareness.
The company implements a service management system based on the "Commodity After-Sales Service Evaluation System" GB/T 27922-2011, establishing a "Service System Manual," "Service Procedure Documents," and "Service Management Documents." This encompasses standardized management of service from basic after-sales service work standards, after-sales service management systems, requirements for personnel interacting with customers, after-sales service performance appraisal systems, to user complaint classification and detailed indicators, and service provision standards.
22
V. Quality Management Foundation
(1) Standard Management
The company integrates enterprise standardization throughout the entire production process. Relevant standards are established for every link, from the procurement of raw and auxiliary materials and packaging materials to the inspection of semi-finished and finished products. This ensures that the entire production process, from the entry of raw and auxiliary materials to the shipment of finished products, is under standardized and regulated management, laying a solid foundation for stabilizing product quality and improving enterprise management levels.
Figure 3 Quality Management System Document Planning Table (See Management Manual)
Figure 4 Order Acceptance and Review Process (Product and Service Requirements) (See Management Manual)
Figure 5 Supplier Management and Procurement Management Process (External Provision Process, Product and Service Control) (See Management Manual)
- Metrology Management
The company strictly implements documents and regulations such as the "Measurement Law of the People's Republic of China." A complete set of management documents and control methods has been established for various stages, including raw material procurement, process management, production equipment, inspection equipment, process inspection, and finished product inspection. Dedicated and part-time metrology personnel are responsible for the management, allocation, and regular calibration of the company's in-use measuring equipment. Emphasis is placed on professional training for metrology management personnel, providing strong support for the standardization of the company's metrology management.
To ensure product quality, strict process control is implemented in the product production process, and metrology management is strengthened for raw and auxiliary materials, etc., in the production process to ensure the normal operation and accuracy of measuring equipment.
The company strictly follows the approval plan and management procedures for the procurement, warehousing, and delivery of measuring instruments. The warehouse has dedicated personnel to manage measuring instruments, establishing account books and registration procedures. The use of measuring instruments must pass verification, and only those with a valid verification certificate can be put into use; in-use measuring instruments are strictly calibrated according to the cycle, strengthening on-site inspections and supervision, understanding their usage, and addressing problems promptly; corrective opinions are provided to departments with problems, and active and effective measures are taken for rectification, laying a solid metrological foundation for the production of high-quality products.
(3) Certification Management
The company has currently passed ISO9001 quality certification and various product certifications, and is preparing for "Made in Zhejiang" brand certification. The company will strictly follow the international quality management system to ensure the quality of its products, thereby ensuring that the company's quality policy of "Customer is our top priority, meticulous work, compliance with regulations, continuous improvement, energy saving and emission reduction, pollution reduction and efficiency improvement, health protection
23
Safety first, environmental protection, risk avoidance" can be successfully implemented. Since its establishment, the company has never experienced
major quality complaints, and the pass rate has reached 100% in annual inspections by various levels of quality and technology departments.
(4) Inspection and Testing Management
The company has purchased a large number of advanced equipment for testing, including energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, spectrometer ROHS software, spectrometer thickness analysis software, and microcomputer-controlled electronic universal testing machine.
The company conducts inspection and testing of incoming goods to ensure that the materials provided by suppliers meet the specified requirements. The quality department is responsible for compiling incoming inspection and testing procedures and for random inspections of incoming materials; the procurement department is responsible for non-conforming materials, and the material warehouse is responsible for checking the quantity, name, and weight of incoming materials.
To ensure that all products pass the specified inspection before entering the next process, the company has formulated "Nonconforming Product Control Procedures," "Shipment Inspection Control Procedures," and "Final Inspection Control Procedures" to conduct strict process inspections and tests. The quality department is responsible for formulating process and final inspection and testing procedures, establishing final inspection points, and organizing process inspection work; quality inspectors are responsible for checking inspection points, semi-finished products, and finished products; and production workers in each workshop are responsible for self-inspection.
Table 7 Testing Equipment Used by the Company
| Serial Number |
Equipment Name |
Unit |
Actual Quantity |
| 1 |
Zoller Tool Testing Instrument |
Unit |
1 |
| 2 |
Klingelnberg Measuring Center |
Unit |
2 |
| 3 |
Gear Radial Runout Tester |
Unit |
2 |
| 4 |
Hardness Tester |
Unit |
1 |
| 5 |
WANGONG Display |
Unit |
1 |
| 6 |
Pneumatic and Electric Electronic Column |
Unit |
1 |
24
VI. Product Quality Responsibility
(1) Product Quality Level
1. Quality Level
The company continues to expand its "refined, specialized, and innovative" R&D team, continuously improving product technology levels and quality performance. In recent years, products have repeatedly received recognition from customers and peers,
Table 8-1 Performance Results Related to Quality Management Level
| Service Performance Indicators |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
| First-time Inspection Pass Rate (%) |
94.65 |
95.87 |
96.34 |
| Return Rate (%) |
2.6 |
2.4 |
2.2 |
| Customer Customization Achievement Rate (%) |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
| Contract Fulfillment Rate (%) |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
| Customer Complaint Handling Rate (%) |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
| Customer Complaint Handling Satisfaction (%) |
95.5 |
96.0 |
98.0 |
2. Product and Service Innovation
Regarding the current state of the gear hobbing cutter market, the demand for gear hobbing cutters of different grades in the domestic market is constantly increasing. Foreign famous brands are penetrating the domestic high-end product market, intensifying competition across the industry, and strengthening brand awareness.
In 2023, the brand upgraded and proposed a new concept of "活力上优.保持热爱" (Vitality Shangyou. Maintain Passion). Shangyou encourages every urbanite to travel and exercise more, live vibrantly, and maintain a positive attitude towards life's beautiful things, striving to allow users to enjoy and experience a wonderful day through healthy and innovative Shangyou products.
Table 13 Company Patents (Partial)
| Serial Number |
Patent Name |
Patent Number |
| 1 |
A kind of rectangular spline alloy hobbing cutter |
ZL 2022 2 2223097.5 |
| 2 |
A kind of worm hobbing cutter |
ZL 2022 2 2157492.8 |
| 3 |
A kind of asymmetrical pressure angle worm wheel hobbing cutter |
ZL 2022 2 1096173.4 |
| 4 |
A kind of new broaching cutter |
ZL 2021 2 0868539.4 |
| 5 |
An invention patent for a worm wheel hobbing cutter that prevents damage from chip adhesion |
ZL 2020 1 1380532.4 |
| 6 |
A kind of pre-grinding broaching cutter |
ZL 2022 2 2196733.X |
| 7 |
A machine tool for processing the return stroke groove of a shaving cutter |
ZL 2017 1 1174434.3 |
| 8 |
A kind of direct-spray quick-cooling broaching cutter assembly |
ZL 2022 2 2521453.1 |
| 9 |
A kind of hobbing cutter that eliminates tool wear and machining accuracy by adjusting the cutter head |
ZL 2021 1 0536927.7 |
| 10 |
A kind of helical full-cut broaching cutter |
ZL 2023 2 0959621.7 |
| 11 |
A kind of high-precision cutting blade |
ZL 2023 2 0983679.5 |
| 12 |
A kind of gear hobbing milling cutter blade |
ZL 2023 2 2351657.X |
| 13 |
A kind of rod-type double hobbing cutter |
ZL 2023 2 2262893.4 |
| 14 |
A kind of large helix angle worm hobbing cutter |
ZL 2023 2 2241265.8 |
| 15 |
A kind of new type of insert gear hobbing cutter |
ZL 2023 2 2624803.1 |
| 16 |
A kind of full-cut hobbing cutter |
ZL 2023 2 1853691.0 |
| 17 |
A kind of hobbing cutter for gear processing |
ZL 2024 2 1766897.4 |
| 18 |
A kind of special-shaped insert blade |
ZL 2024 2 1766646.6 |
(II) Product After-Sales Responsibility
1. Strengthen customer relationship management through multiple channels
The company strengthens customer relationship management through multiple channels and strengthens after-sales management:
(1) By establishing extensive customer relationships, providing feedback channels in multiple ways and comprehensively, quickly processing customer information, and continuously improving service quality. Maintaining customer relationships is not just the work of the after-sales service department, but a process involving all staff. The company adheres to the service philosophy of "feedback in the first instance" to provide services, ensuring customer satisfaction through comprehensive services across various channels.
(2) Once a customer establishes a cooperative intention with the company, the company will maintain communication with the customer from aspects such as product research and development, implementation, monitoring, and service, establishing a comprehensive cooperative relationship. All resources can be mobilized to provide services to customers. In recent years, the company has been committed to transforming from a traditional manufacturing enterprise into an enterprise providing comprehensive services, being market and customer-oriented, and continuously meeting customer needs.
(3) The sales department promptly feeds back relevant information to customers based on customer orders, and makes timely adjustments to meet customer needs if there are any changes during the process.
(4) The company establishes information transmission channels for customers, mainly including the following:
Professional customer service personnel collect information through telephone, fax, email, QQ, and WeChat;
Entrusting third-party surveys to provide feedback;
Establishing a WeChat public platform to transmit information;
Various inquiry and feedback information channels to obtain opinions, suggestions, and complaints.
(5) After customer information obtained through various channels is summarized by the sales department, it is quickly transmitted within the company. All customer information is filed as important data. Regarding the problems and defects reflected, it is promptly transmitted to various departments to promote improvement. Business
26
personnel and service personnel act as the company's representatives for customers, responsible for supervising the completion of complaint handling by various departments, and
evaluating relevant department heads.
2. Complaint Handling
The after-sales service department is responsible for the management of customer complaint docking. After receiving a customer complaint, the complaint issue is identified and verified within 2 hours. On the one hand, a problem handling plan (including returns, replenishment, etc.) is formulated, and after confirmation by the customer, it is implemented within 24 hours. On the other hand, relevant internal personnel are organized to formulate a rectification plan for the problem and implement it. The internal rectification plan and implementation results are fed back to the customer as needed and confirmed by the customer.
Among them, internal rectification includes both internal rectification within the company and rectification and verification by relevant parties. For the rectification requirements of relevant parties, the Quality Department issues "Corrective and Preventive Measures," which are transmitted to the relevant parties by the Purchasing Department and supervised for implementation. The rectification effect is ultimately verified by the Quality Department.
同时,公司为确保客户投诉及反馈信息的有效利用,每月都会对顾客的投诉进行汇总分析,形成《顾客回馈处理统计表》,由品质部牵头,组织各部门对存在的共性问题进行分析,制定《纠正预防措施》进行改进,整改效果由品质部组织验证,并以电话回访的方式跟踪投诉处理过程,了解顾客的满意度。
同时,公司售后服务部、品质部对客诉信息定期监测,设立质量监测站,对市场中重复发生及影响客户满意度和产品体验的问题进行集中收集,并加以分析,形成报告。定期组织内部各部门召开产品质量会议。组建品管圈、跨部门产品质量改善团队、同时联动上游供应商及相关合作伙伴,对重大产品质量问题进行攻坚改善,消除质量风险,提升产品质量满意度。
(三)企业社会责任
公司作为 齿轮滚刀企业,为社会创新价值的同时,积极履行社会责任,全力支持公益事业。在履行公共责任、公民义务、恪守道德规范和保护公众健康、安全、环境等方面,公司从自身生产经营活动出发,分析相关活动对社会产生的影响,积极主动承担责任和义务,并在行业中率先向社会定期发布社会责任报告。
1、公共责任
公司在生产过程中对社会带来的影响因素有粉尘、废气、废水排放等,给环境带来污染,噪声可能会给公众身体带来危害等。
为此,公司贯彻国家《环境保护法》、《大气污染防治法》、《水污染防治法》、《安全生产法》、《消防法》相关法律法规,确立减少污染、排放治理的工作目标,按照“全面规划、合理布局、综合利用、化害为利、依靠群众、大家动手、保护环境、造
27
福人民”的环保方针为指导,设置专门机构负责环境管理。以PDCA循环为手段,建立环境管理体系,通过实施对环境的危害分析、风险评价,落实环境因素识别与评价管理程序、环境监测与测量控制程序、环境条件及设施管理制度、基础设施和工作环境控制程序、环境管理手册。
按照公司制订的安全生产标准化,严格落实安全预防“三同时”、安全事故“不放过”的目标,与各车间主管签订安全生产责任协议,建立安全事故应急小组,定期开展消防演练活动,实现安全生产目标。
根据上述措施,公司确定环境保护、能源利用、安全生产、公共卫生四个方面,确定相关影响指标、风险识别,根据国家相关标准确立测量方法。
表14公共责任控制方法
| 控制 Category |
影响指标 风险评估 |
国家/ 行业标准 |
内控 指标 |
Measurement 方法 |
过程控制及方法 |
|
| 质量安全 |
产品 |
产品安全 |
GBT 6083-2016《齿轮滚刀 基本型式和尺寸》GBT 6084-2016《齿轮滚刀 通用技术条件》等。 |
质量安全事故发生:0起 |
外部检测内部测试检验 |
进行设计FEMA分析 加强工艺纪律检查 严格“四检”制度 加强安装技术指导和监督跟踪提供操作培训 |
| 生产安全 |
运营 |
有害物质 |
《职业病防治》 |
职业病零 |
月度统计 |
定期将员工及时调换至其他岗位 利用先进设备超声波进行自动化 清洗 |
| 机械损伤:导致人员伤亡 |
《安全生产法》、《浙江省安全生产管理条例》 |
重大伤亡:0;轻伤:<10次 |
员工定期进行安全教育 特种设备定期检验 工厂现场佩戴安全帽 定期开展安全检查 |
|||
| 火灾:导致财产损失及人员伤亡 |
《消防法》、《机关、团体、企业、事业单位消防安全管理规定(公安部61号令)》 |
无火灾事故发生 |
员工定期进行消防安全知识教育定期进行消防演练 开展安全检查,消除火灾隐患 |
|||
| 环保 |
运营 |
三废 |
《大气污染物综合 排放标准》、《污 水综合排放标准》 |
排放达标 |
公司内部检测、环境部门检测 |
加大了产品结构调整力度,投入资金500多万元增加环保设备,改善环保问题 |
| 噪音:导 致环境污 染 |
《工业企业厂界环 境噪声排放标准》 等 |
3类≤ 65dB(A) |
||||
| 节能 |
运营 |
节能 |
《节约能源法》 |
Ten thousand yuan energy consumption |
Annual Statistics |
Advocating for energy saving Reducing energy consumption through equipment upgrades and the promotion of new technologies and processes Reducing energy consumption through new technologies and processes |
| 控制 Category |
影响指标 风险评估 |
国家/ 行业标准 |
内控 指标 |
Measurement 方法 |
过程控制及方法 |
|
| 产品 |
Single unit energy reduction (kW) |
Single unit Statistics |
Adopting stable and efficient high-frequency power supplies to effectively reduce Low energy consumption |
|||
| Resource integration and utilization |
运营 |
Resource utilization |
The Circular Economy Law |
Material utilization Rate |
Annual Statistics |
Advocating for waste recycling Reducing energy consumption through equipment upgrades and the promotion of new technologies and processes New processes to improve resource utilization |
| Public health |
运营 |
Living garbage, production waste, idle items, dust, and stains |
Cleanliness and hygiene |
Factory 5S management |
Public health inspection |
Strictly enforce the company's management manual Routine inspection |
Company senior management uses external audit methods in strategic environmental analysis, and uses industry and network channels to conclude that product safety, environmental protection, energy consumption, safety production, and public health will have a significant impact on the company's future products and operations.
Table 15: Foresight and Response to Public Responsibility
| Public concerns |
Content description |
Countermeasures |
| Concerns about public health |
Occurrence of public health events |
ü Equip sufficient protective gear ü Conduct physical examinations and vaccinations for relevant personnel ü Develop contingency plans ü Strengthen internal enterprise medical management |
| Concerns about safety production |
Safety accidents Occupational health hazards |
ü Establish an occupational health and safety management system ü Develop contingency plans |
| Concerns about product quality and safety |
Human health and safety |
ü Promote clean production ü In the application of new materials |
| Concerns about the company's environmental protection in production |
Sewage, noise, energy consumption |
ü Use green resources ü Establish contingency plans |
2. Moral integrity
For a long time, the company's senior leaders, starting from the core values of the enterprise, have attached great importance to the cultivation of enterprise moral culture in the process of implementing enterprise culture construction, and have strived to create a good atmosphere of advocating moral cultivation, with senior leaders leading by example and all employees actively participating. The company establishes a sound company management system in accordance with national laws and regulations such as the Company Law, the Accounting Law, and the Labor Law; senior managers strictly manage themselves and set an example as law-abiding role models. Since its establishment, the company has operated in accordance with the law, and none of its senior managers have violated laws or regulations.
The company has dedicated legal personnel and an internal audit department that conducts audits every quarter and legal education every month to standardize, guide, and supervise the business conduct and transactions of various departments, operate in accordance with the law, and improve the concept of professional law-abiding.
Abide by social moral norms, operate with integrity, and abide by laws and regulations. Properly handle relationships with customers, investors, partners, banks, and society, emphasizing credibility, commitment, contracts, and credit, and achieving sincere cooperation and mutual benefit.
The company has formulated strict codes of conduct and set standards for how to maintain the company's values in work and communication with clients and other groups. The company's internal audit office is responsible for analyzing and handling violations, errors, and dereliction of duty, or proposing disciplinary suggestions, which are then handled by the management committee. The company takes a zero-tolerance attitude towards commercial corruption, focusing on the guiding, punitive, and regulatory functions of the system. It has successively formulated and issued regulations such as the "Implementation Rules for Integrity Construction," "Sunshine Agreement for Outsourcing Product Procurement," "Code of Conduct for Leading Cadres," and "Bidding Management Regulations," requiring employees and management personnel to follow the highest standards of business ethics and comply with the laws and regulations of the countries or regions where the company's business is located to prevent potential risks in terms of ethical norms and compliance, establish ethical models, and promote continuous improvement in compliant operations.
The company pays attention to publicity and education on anti-commercial bribery and anti-improper internal transactions, strengthening the moral integrity education of employees ideologically. In employee onboarding training, enterprise culture and moral integrity, and employee conduct norms education are included. Through positive guidance and negative warnings, an atmosphere of integrity and honesty is created within the company, so that employees remember that integrity construction is the foundation of the enterprise's survival, and integrity in work is the guarantee of personal career development.
The company has established measurement methods and indicators for supervising moral behavior.
Table 16: Measurement Methods and Indicators for Moral Behavior Control
| System |
Object |
Integrity principles Ethical standards |
Supervisory department |
Monitoring indicators |
Guaranteeing measures |
| Employee integrity and ethics system |
Middle and senior level Leaders |
Diligence, integrity, and efficiency |
Shareholders' meeting, board Of directors, internal audit department |
Integrity record, evaluation score Points, crime rate |
Ideological and moral education, integrity education Accept democratic assessments and regular audits, Supervision and inspection |
| Ordinary Employees |
Integrity, law-abiding, and compliance |
Party branch, office Room |
Number of violation reports, violations Crime rate |
Ideological and moral education, internal discipline inspection Check |
|
| Company's integrity and ethics system |
Employees |
Care, respect |
Trade union |
Employee satisfaction, key Key position employee turnover rate |
Create a respectful humanistic environment, build Establish an innovative training mechanism, improve Development incentive system |
| Supplier |
Expand suppliers, optimize supply Party, invest in suppliers, develop Supplier |
Supplier |
Supplier satisfaction, payment Payment timeliness |
Pay on time, cooperate amicably |
|
| Customer |
Quality wins the market, service Service guarantees the market, technology Leads the market |
Customer |
Contract fulfillment rate, customer Satisfaction |
Provide high-cost-effective products and high-quality services Service |
|
| Society |
Give back to the public |
Government, community |
Credit rating, tax and Timeliness, environmental compliance rate, Public welfare investment |
Tax compliance, three wastes and noise control Control, enthusiastic about public welfare undertakings |
|
| Shareholder |
Effectively protect shareholder interests, Especially those of small and medium-sized shareholders |
Board of directors |
Owners' equity |
Stable dividends, timely and publicly available information Disclosure |
29
3. Public welfare support
Support public welfare undertakings, identify key support areas: Company senior leaders, in accordance with the sense of responsibility to revitalize the local economy and give back to society, closely following the core values of "excellence, innovation, expansion, and integrity," based on the company's development direction and strategic priorities, support local economic and industry development, education and culture, public facilities construction, environmental protection, and charitable causes as key support areas for public welfare undertakings, and actively and effectively carry out public welfare activities.
Table 17 Company Public Welfare Support Activities
| Donation Name |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
| Poverty Alleviation Village Pairing Assistance |
30,000 yuan |
40,000 yuan |
40,000 yuan |
| Charity Federation/Branch |
50,000 yuan |
50,000 yuan |
100,000 yuan |
| Employee Assistance |
33,000 yuan |
36,000 yuan |
45,000 yuan |
| Blood Donation and Volunteer Activities |
29 person-times |
32 person-times |
35 person-times |
Company leaders lead by example, employees actively participate: Remembering our roots in pursuing wealth, giving back to society. Company senior leaders attach importance to social responsibility, lead by example, care for employees in difficulty, establish "employee medical mutual aid," carry out heartwarming projects, take the lead in donating money and materials, and employees also actively participate, giving back to the country and society with practical actions. In order to solve the problem of employee medical mutual aid security, combining the actual situation of our company, we establish employee medical mutual aid at the beginning of each year to achieve the purpose of having medical security, benefiting many employees.
(IV) Quality and Credit Record
Since its establishment, the company has never experienced any major quality complaints, and the pass rate has reached 100% in the annual inspections by various levels of quality and technology departments. The company has also received numerous commendations and awards from government authorities and industry associations for its product quality:
"Zhejiang Province High-tech Enterprise"
"Zhejiang Province Specialized, Refined, and Unique Small and Medium-sized Enterprise"
"Zhejiang Province High-tech Enterprise Research and Development Center"
30
Report Conclusion
Prospect
Implementing social responsibility management is a crucial measure for Shangyou to adapt to the global trend of enterprise development, enhance its competitiveness, and influence. As a leading enterprise in the field of gear hobbing cutters, Shangyou learns from and draws on the advanced management experience of world-class enterprises, regards the fulfillment of social responsibility as an important way to enhance the company's comprehensive strength, actively responds to various opportunities and challenges, promotes the scientific development of the enterprise, and strives to build an enterprise with unique characteristics and competitiveness in the field of gear hobbing cutters, promote the rapid development of the national high-tech industry, and truly achieve "Made in China."
Reader Feedback
Thank you for taking the time to read Zhejiang Shangyou Cutting Tools Co., Ltd.'s 2024 Enterprise Quality and Integrity Report.
There may be some flaws and omissions in the preparation of this report. We are very willing to listen to your opinions and suggestions to help us continuously improve the report preparation methods and social responsibility performance.
Contact Us
This report is in Chinese. For a printed copy, please contact:
Company: Zhejiang Shangyou Tool Co., Ltd.
Address: No. 9, Street 25, Dongbu New District, Wenling City, Zhejiang Province
Postcode: 317527
Tel: 0576-86997666
Fax: 0576-86985688
Email: cici@shangyoutools.com sales@shangyoutools.com
Meanwhile, you can download the electronic version of this report from Shangyou's website: www.shangyoutools.com
Zhejiang Shangyou Tool Co., Ltd.
Report Compilation Date: February 2025
32
Related
2025-05-29
2025-05-29







